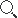Plate heat exchangers are high-efficiency, energy-saving, and environmentally friendly heat exchange equipment that can be widely used in fields such as chemical, pharmaceutical, metallurgical, electrical, textile, and environmental protection. There are two main types of liquid flow in plate heat exchangers:
Convective flow
Convective flow refers to the flow of liquid through a series of plates in a plate heat exchanger from bottom to top or from top to bottom, transferring heat through convection. There are two ways for liquid to flow in a plate heat exchanger: single pass flow and double pass flow. Single pass flow refers to the flow of liquid only within one plate string, while double pass flow refers to the alternating flow of liquid between two plate strings.
Mixed flow
Mixed flow refers to the simultaneous convection and transverse flow of liquid in the plate heat exchanger. The flow rate changes greatly, forming secondary flow, etc., thus generating more turbulence and accelerating heat transfer. The mixed flow method is more suitable for heat exchange during condensation or evaporation processes, and is also commonly used in heat exchange processes containing high concentration solid particles or viscous liquids, which can effectively prevent particle blockage and shell pollution.
Whether it is convective flow or mixed flow, plate heat exchangers can achieve the best heat transfer effect by adjusting parameters such as plate spacing, plate wave number, and liquid flow rate. Among them, the flow rate and flow mode of the liquid have an important impact on the heat transfer efficiency of the heat exchanger. In practical applications, it is necessary to select appropriate liquid flow methods based on the characteristics of the liquid and the required heat exchange process to improve the performance and efficiency of the heat exchanger.
abstract
Plate heat exchangers are widely used in the field of heat exchange. Due to their high heat transfer efficiency, compact structure, and ease of cleaning and maintenance, they have been widely used in various fields in recent years. This article focuses on the working principle, structural characteristics, and application fields of plate heat exchangers, with a focus on introducing research achievements in optimizing the structure and improving heat transfer efficiency of plate heat exchangers. In addition, the article also explores the application of combining plate heat exchangers with other advanced technologies to achieve more efficient energy utilization and environmental protection.
introduction
A plate heat exchanger is a device that transfers heat between two different media. The device is composed of multiple thin plates stacked together, separated by sealing gaskets between the plates, and heat transfer is achieved through certain thin plate gaps. Plate heat exchangers are widely used in industries such as chemical, pharmaceutical, and construction due to their high heat transfer efficiency, compact structure, and ease of cleaning and maintenance.
working principle
The working principle of plate heat exchangers is very simple. Through the thin plate gap inside the plate heat exchanger, the hot and cold media that need to be heated or cooled flow on the opposite side, and transfer heat through a certain flow rate and heat transfer area formed between the thin plates. Thin plates are usually designed in a corrugated form to increase the contact surface area and promote the heat transfer process.
Structural characteristics
The structural characteristics of plate heat exchangers mainly include corrugated plates, rubber gaskets, and extruded seals. Among them, corrugated plates are used to achieve clearance between partitions; Rubber gaskets are used to ensure the sealing of the entire plate heat exchanger; Extruded seals are used to reduce the risk of leakage and reduce vibration noise. In addition, plate heat exchangers have different structural forms in different application scenarios, such as fully sealed plate heat exchangers, semi sealed plate heat exchangers, etc.
application area
Plate heat exchangers are widely used in fields such as chemical, pharmaceutical, and construction. In the chemical and pharmaceutical industries, plate heat exchangers are used for production processes such as chemical reactions, heating, cooling, evaporation, and dehydration. In the field of construction, plate heat exchangers are used in systems such as underfloor heating, air conditioning, and heat pumps.
Structural improvement
Structural improvement is an important research direction in the field of plate heat exchangers. By optimizing the structural design of corrugated plates, as well as using new materials to make thin plates, cutting techniques, and precision welding techniques, higher heat transfer efficiency and better durability can be achieved.